Imagine a scenario in which employee productivity is hampered by human resource management’s tangle of paperwork. These problems are frequent and can prevent companies from realising their full potential. This is where the SAP Course help and become the backbone of many successful organisations, enabling them to navigate the complexities of the modern business landscape with ease. But before moving ahead, individuals should have a brief understanding of What is SAP and its modules, and that’s what we’re about to explore in this blog.
Table of Contents
1. What is SAP?
2. Exploring Core SAP Modules
3. Specialised SAP Modules
4. Benefits of Learning Different SAP Modules
5. Conclusion
What is SAP?
SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing) is a complete suite of business solutions meant to revolutionise the way organisations function. SAP was founded in the early 1970s by five IBM engineers and has since evolved into one of the world’s major enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, servicing a wide range of sectors worldwide.
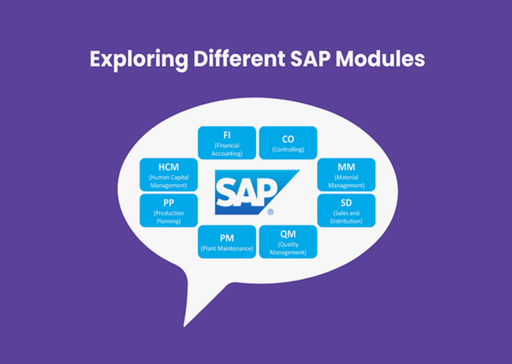
Exploring Core SAP Modules
1. SAP Finance (FI) Module
The SAP Finance Module serves as the foundation of financial management. It is in charge of all financial activities, such as accounts payable and receivable, asset accounting, and general ledger operations. This module provides a complete picture of a company’s financial situation, allowing for more informed financial planning and analysis.
2. SAP Human Capital Management (HCM) Module
3. SAP Sales and Distribution (SD) Module
The SAP SD Module oversees sales, distribution, and customer service. It handles sales orders, pricing, shipping, and billing, ensuring order-to-cash procedures run smoothly. Businesses can use the SAP SD Module to increase customer happiness, sales processes, and revenue generation.
4. SAP Material Management (MM) Module
Businesses engaged in manufacturing and commerce need to handle materials and resources effectively. Procurement, inventory control, material valuation, and vendor assessment are all managed by the SAP MM Module. This module helps firms cut expenses, minimise stockouts, and streamline procurement procedures by streamlining the supply chain.
Specialised SAP Modules
1. SAP Business Intelligence (BI) Module:
It allows businesses to collect, analyse, and visualise data, converting raw data into meaningful insights. This module enables organisations to make educated strategic decisions by providing robust reporting and analytics capabilities.
2. SAP Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Module
A successful business is built on the foundation of satisfied customers. Effective customer engagement, sales management, and marketing campaigns are made possible by the centralisation of customer-related data and interactions through the SAP CRM Module. Improved client relations help firms increase revenue and foster customer loyalty.
3. SAP Supply Chain Management (SCM) Module
The intricacies of the supply chain necessitate sophisticated solutions. Supply chain functions such as demand planning, production scheduling, inventory management, and logistics are all optimised using the SAP SCM Module. This module helps firms decrease costs, improve productivity, and improve customer experience by assuring supply chain visibility and collaboration.
4. SAP Advanced Planning and Optimization (APO) Module
The SAP APO Module elevates supply chain management. It offers advanced forecasting, planning, and optimisation features. Businesses can align their supply chain processes with market trends by improving their production, distribution, and inventory management. Businesses may respond swiftly to shifts in the market and customer needs with the aid of this module.
Benefits of Learning Different SAP Modules
1. Enhanced Business Efficiency:
SAP Modules boost operational efficiency by automating procedures, minimising manual errors, and providing real-time data availability. Businesses can boost overall productivity by streamlining procedures, reducing bottlenecks, and streamlining procedures.
2. Career Opportunities:
Acquiring expertise in SAP modules enables individuals to follow multiple career paths. Proficiency with SAP is highly desirable in a variety of industries, making it an advantageous set of skills for career progression.
3. Global Job Market Demand:
SAP expertise is in high demand because of global company expansion. Learning SAP modules Each module provides a distinct layer to the SAP ecosystem, from essential modules like Finance and Human Capital Management to specialised modules like Business Intelligence and Advanced Planning. Individuals can pave the road to fulfilling careers by embracing SAP education, while businesses can optimise their processes and acquire a competitive edge in the market.
Conclusion
We’ll go through the typical blunders covered in this blog post’s conclusion and stress the significance of taking lessons from them. We’ll stress that the process doesn’t end with the interview and promotes ongoing learning and development.